The introduction of USB Type-C has revolutionized the way we connect our devices, offering faster data transfer speeds, improved power delivery, and a more convenient reversible design. However, the transition from the traditional USB Type-A to USB Type-C has not been without its challenges. This article explores the compatibility issues that arise during this transition, providing insights into the implications for consumers, manufacturers, and the tech industry as a whole.
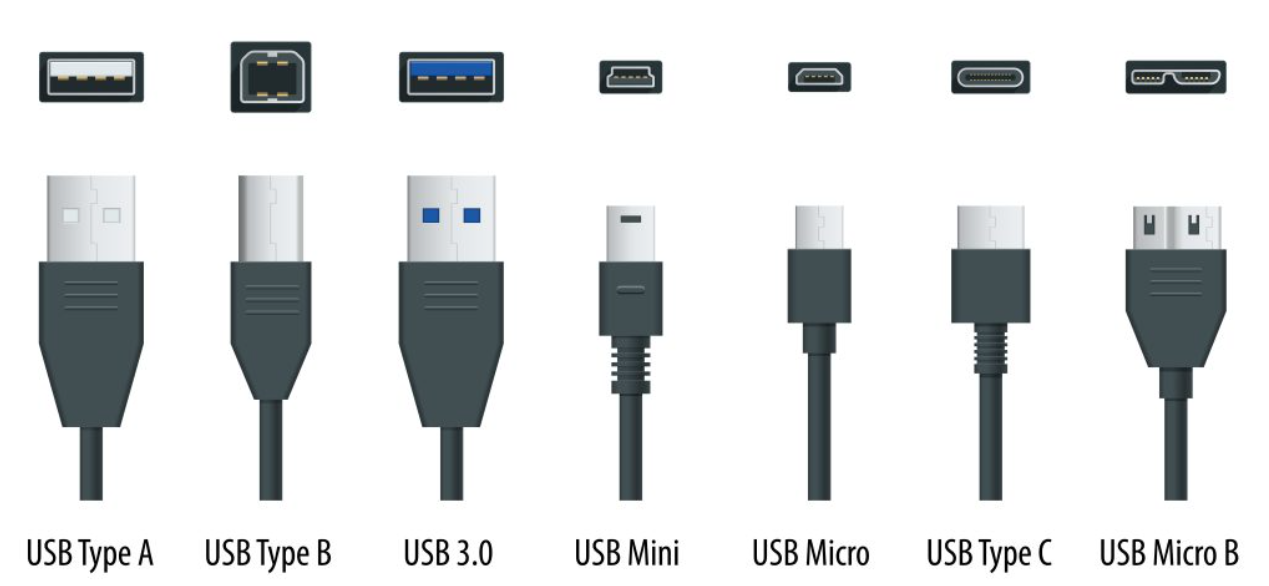
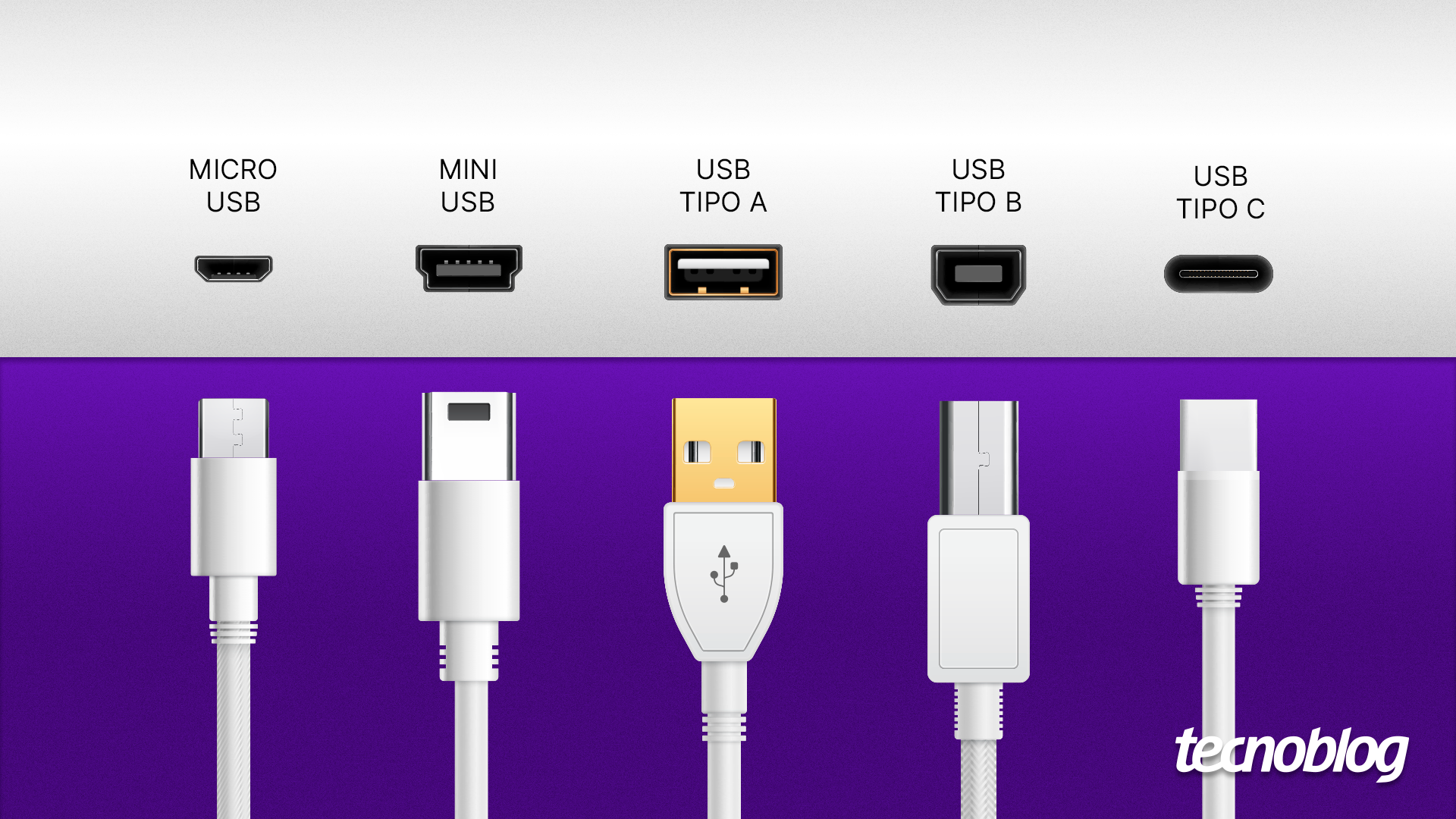
Understanding USB Types: A Quick Overview
To appreciate the challenges associated with the transition from USB Type-A to Type-C, it’s important to understand the differences between these two formats.
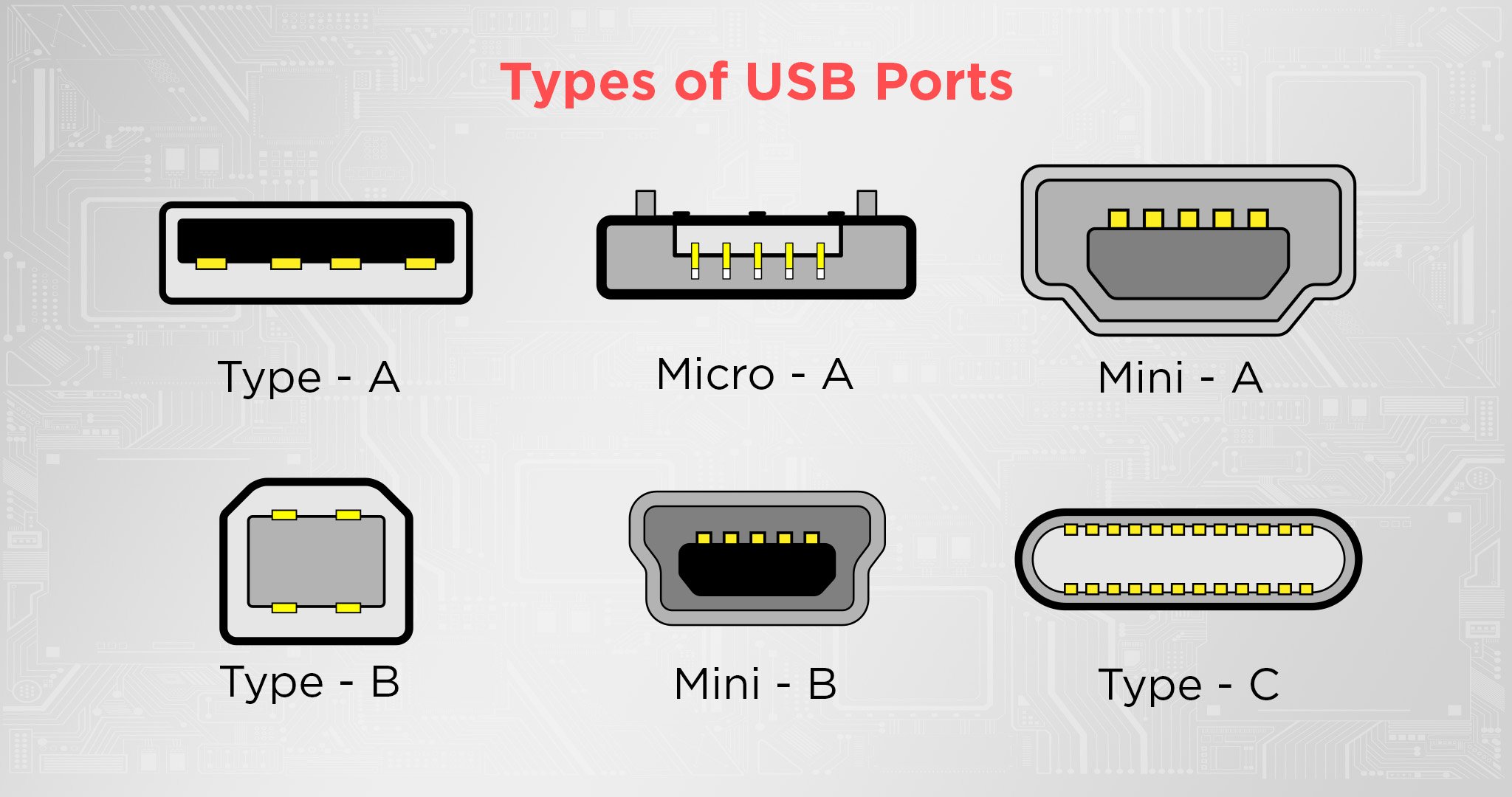
- USB Type-A: This is the standard rectangular connector that has been widely used since the early days of USB technology. It is found on a vast array of devices, from computers to printers.
- USB Type-C: This newer connector features a reversible design, allowing users to plug it in either way. It supports higher data transfer speeds and greater power delivery, making it suitable for a variety of modern devices, including smartphones, laptops, and peripherals.
The Benefits of USB Type-C
Before diving into the compatibility issues, it’s essential to recognize the benefits of USB Type-C, which are driving its adoption:
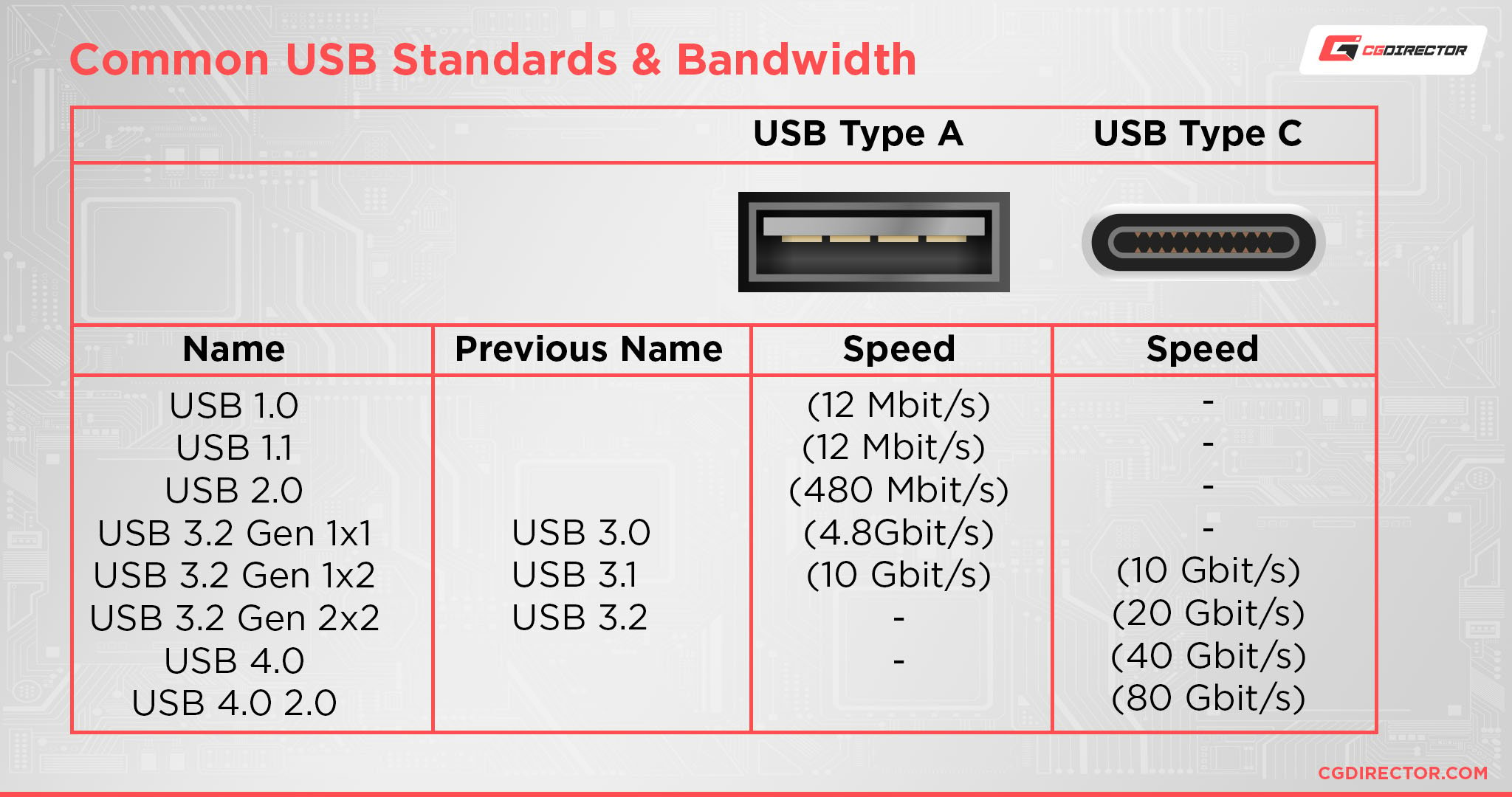
- Faster Data Transfer: USB Type-C supports data transfer speeds of up to 40 Gbps with Thunderbolt 3, compared to the maximum 5 Gbps of USB 3.0 Type-A.
- Increased Power Delivery: USB Type-C can deliver up to 100 watts of power, allowing for faster charging of devices, including laptops.
- Universal Compatibility: With a single connector type, USB Type-C aims to reduce the number of cables and adapters consumers need.
Compatibility Challenges in the Transition
Despite its advantages, the transition to USB Type-C has introduced several compatibility challenges:
1. Device Compatibility
Many consumers still own devices that use USB Type-A, leading to immediate compatibility issues:
- Legacy Devices: Printers, external drives, and older laptops primarily use USB Type-A, making it difficult for users to connect these devices to newer hardware.
- Adapters and Dongles: The need for adapters can lead to added costs and inconvenience for users who want to connect older devices to new systems.
2. Peripheral Compatibility
Peripheral devices such as keyboards, mice, and game controllers are also affected:
- Limited Availability: While many peripherals now come with USB Type-C connectors, a substantial number still rely on the Type-A standard.
- Functionality Issues: Some devices may require specific drivers or software that may not be available for USB Type-C peripherals.
3. Software and Driver Issues
Software compatibility is another area of concern:
- Driver Availability: Some older devices may not have updated drivers to support USB Type-C, limiting functionality.
- Operating System Support: Certain operating systems may not fully support USB Type-C features, such as power delivery or data transfer speeds.
Case Studies: Real-World Impact of Compatibility Issues
The impact of these compatibility issues can be observed in various case studies:
Case Study 1: The Consumer Electronics Industry
In 2018, a survey conducted by the Consumer Technology Association revealed that:
- Approximately 60% of households reported owning at least one device that still relied on USB Type-A.
- Consumers expressed frustration over needing multiple cables and adapters to connect devices, leading to a demand for more USB Type-C products that can also accommodate Type-A devices.
Case Study 2: The Gaming Community
The gaming community has also felt the effects of the transition:
- Many gaming peripherals, such as controllers and headsets, continued to use USB Type-A connectors, limiting compatibility with new gaming consoles that only feature USB Type-C ports.
- Gamers have reported having to invest in new peripherals or adapters, which can be costly and inconvenient.
Solutions to Compatibility Issues
Addressing these compatibility challenges requires a multi-faceted approach:
1. Increased Adoption of Adapters

Manufacturers are producing a wider range of adapters to bridge the gap between USB Type-A and Type-C:
- Adapters that convert Type-C to Type-A are becoming more common, enabling users to connect older devices seamlessly.
- Multi-port adapters that support USB Type-C, Type-A, HDMI, and other connections are gaining popularity, offering versatility for users.
2. Encouraging Universal Standards

The tech industry is moving towards standardizing connectors:
- Organizations like the USB Implementers Forum are working to promote USB Type-C as the universal standard for all devices.
- Collaborations between manufacturers can lead to the development of devices that natively support both USB Type-A and Type-C.
3. Consumer Education
Educating consumers about the transition can help mitigate frustrations:
- Providing clear information about compatibility and available adapters can assist consumers in making informed purchasing decisions.
- Manufacturers can offer guidance on selecting devices that will work seamlessly together.
Future Outlook: USB Type-C and Beyond

The future of USB technology is undoubtedly leaning towards USB Type-C. As manufacturers phase out USB Type-A connectors, compatibility issues are expected to diminish over time:
- As more devices adopt USB Type-C, the need for adapters will lessen, simplifying the user experience.
- Emerging technologies may introduce even more advanced features, such as faster charging and data transfer speeds, further solidifying USB Type-C’s role in the tech ecosystem.
The transition from USB Type-A to Type-C presents a complex landscape of compatibility issues that affect consumers, manufacturers, and the broader tech industry. While the benefits of USB Type-C are clear, the challenges posed by legacy devices, peripheral compatibility, and software issues cannot be overlooked. However, through increased adoption of adapters, standardization efforts, and consumer education, the industry is actively working to address these challenges. As we look to the future, the widespread adoption of USB Type-C will undoubtedly pave the way for a more streamlined and efficient technology ecosystem.


